Common Manufacturing Challenges in Drones and How 3D Printing Solves Them
The drone industry is evolving at a rapid pace, with applications expanding across defense, agriculture, surveying, logistics, infrastructure inspection, and industrial automation. While drone capabilities continue to grow, manufacturing UAV components remains a complex challenge. Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle to keep up with the demand for lightweight structures, rapid iterations, and cost-efficient production.
This is where 3D printing has emerged as a powerful solution addressing long-standing drone manufacturing challenges while enabling faster innovation and scalable production.
1. Weight Reduction Without Compromising Strength
The Challenge: Drones must be lightweight to maximize:
-> Flight time
-> Payload capacity
-> Energy efficiency
Conventional manufacturing methods often require thicker walls or multiple fasteners, adding unnecessary weight and structural complexity.
How 3D Printing Solves It: Additive manufacturing enables
-> Topology-optimized designs
-> Lattice and honeycomb structures
-> Part consolidation
These design freedoms allow drone frames and components to be strong exactly where needed without excess material. Technologies like HP Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) and Metal 3D printing are widely used to produce lightweight yet durable UAV structures.
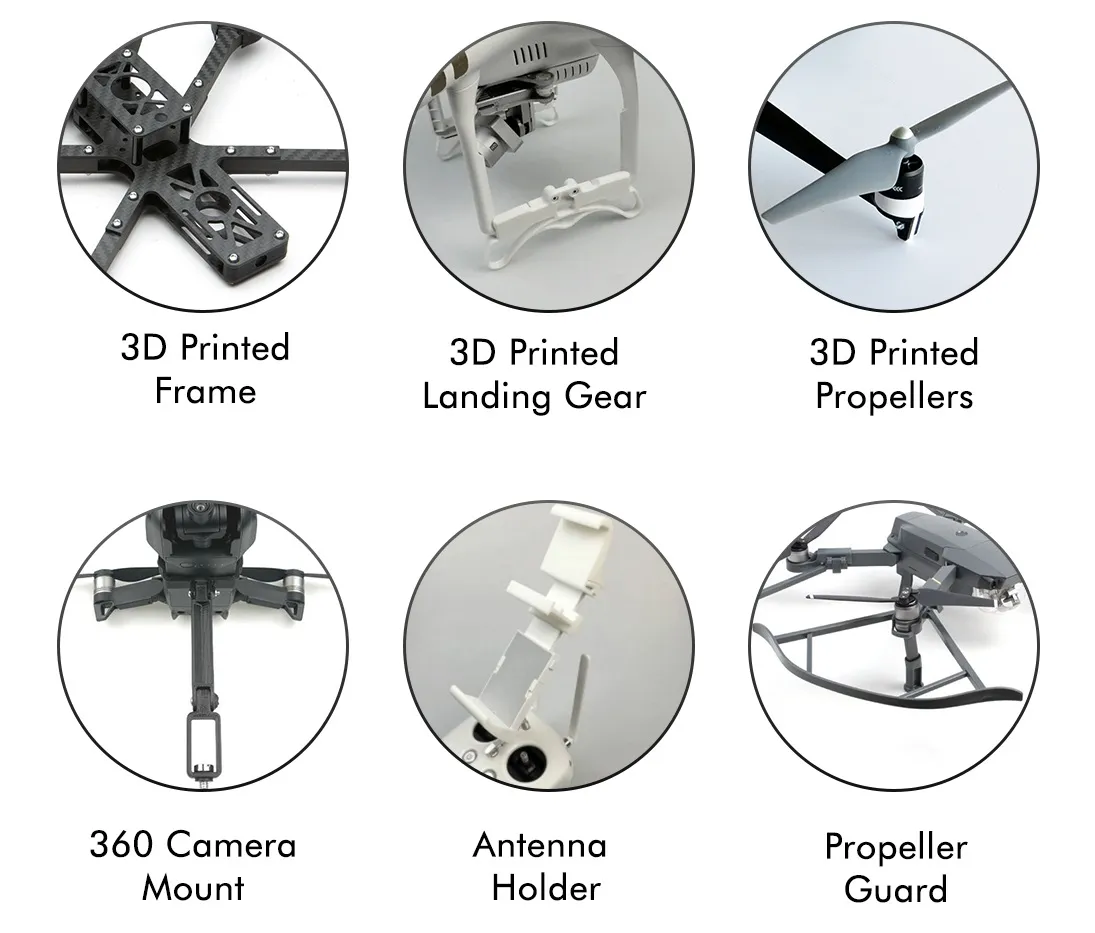
2. Complex Geometries and Integrated Designs
The Challenge: Modern drones integrate multiple systems - wiring channels, cooling ducts, mounts, sensors, and housings - within extremely compact spaces. Traditional machining often limits design freedom or requires assembly of multiple parts.
How 3D Printing Solves It: 3D printing allows engineers to:
-> Manufacture complex internal geometries
-> Integrate multiple functions into a single part
-> Reduce fasteners and assembly steps
This leads to improved structural integrity, reduced failure points, and simplified production workflows.
3. Rapid Prototyping and Design Iterations
The Challenge: Drone development cycles are fast, and designs evolve frequently based on testing, regulations, and performance feedback. Conventional tooling significantly slows down iteration.
How 3D Printing Solves It: With additive manufacturing, teams can:
-> Prototype new drone components in days instead of weeks
-> Test multiple design versions simultaneously
-> Implement quick design changes without tooling costs
This speed is especially critical for startup UAV companies and R&D teams racing to validate designs and reach the market faster.
4. High Cost of Low-Volume Production
The Challenge: Many drone applications require low- to medium-volume production, especially for specialized or mission-specific UAVs. Traditional injection molding or CNC machining becomes expensive at low quantities.
How 3D Printing Solves It: 3D printing eliminates tooling costs and allows:
-> Cost-effective batch production
-> Scalable production without major upfront investment
This makes additive manufacturing ideal for custom drones, defense prototypes, and industrial UAVs.
5. Customization and Application-Specific Designs
The Challenge: Different drone applications require unique designs—whether for payload mounts, aerodynamic housings, or structural reinforcements. Traditional manufacturing lacks flexibility for frequent customization.
How 3D Printing Solves It: Additive manufacturing enables
-> Application-specific drone frames
-> Custom mounts and enclosures
-> Region- or mission-specific modifications without redesigning entire tools
Each drone can be optimized for its exact operational environment.
6. Material Performance and Durability
The Challenge: Drone components must withstand vibration, heat, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress - especially in industrial and defense applications.
How 3D Printing Solves It: Additive manufacturing enables
-> PA12 and glass-filled polymers
-> High-strength aluminum and steel alloys
-> Heat and chemical-resistant polymers
allow drone manufacturers to meet demanding performance requirements while maintaining lightweight construction.
7. Faster Time-to-Market
The Challenge: The drone market is highly competitive. Delays in manufacturing can result in lost opportunities.
How 3D Printing Solves It: By combining design, prototyping, and production into a single digital workflow, 3D printing:
-> Shortens product development cycles
-> Reduces dependency on external tooling suppliers
-> Enables faster scaling from prototype to production

Why Advanced Manufacturing Matters for Drone Companies
As discussed in our previous blog on 3D printing for drone companies, additive manufacturing is no longer limited to prototyping - it is now a production-ready solution for UAV components.
At Vexma, advanced additive manufacturing plays a key role in helping drone manufacturers move from concept to functional, flight-ready components by combining design for manufacturability, polymer and metal 3D printing, and controlled production workflows under one roof.
Conclusion
Drone manufacturing presents unique challenges from weight optimization and complex geometries to rapid iteration and cost control. 3D printing directly addresses these challenges, offering unmatched design freedom, speed, and production efficiency.
As UAV technology continues to advance, additive manufacturing will remain a critical enabler helping drone companies innovate faster, manufacture smarter, and stay competitive in an evolving aerospace landscape.