The Impact of 3D Printing on Modern Healthcare: From Prototypes to Patient Care
Introduction
The healthcare industry is rapidly embracing advanced technologies to improve patient outcomes, reduce production costs, and accelerate innovation. Among these, 3D printing (additive manufacturing) has emerged as a true game-changer. From patient-specific implants to anatomical models for surgery, 3D printing services are reshaping how the medical sector designs, tests, and delivers care.
1. What Is 3D Printing in Healthcare?
3D printing in healthcare involves using additive manufacturing technologies such as SLA, SLS, and MJF to create medical components layer by layer from digital designs. These parts can include custom prosthetics, surgical instruments, anatomical models, dental devices, and bioprinted tissues.
The ability to print customized, complex, and biocompatible parts has made 3D printing an integral part of modern medical manufacturing.
2. Key Benefits of 3D Printing Services in Healthcare
a. Personalized Patient Care
Every patient is unique, and so are their medical needs. 3D printing enables customized implants, prosthetics, and surgical tools tailored precisely to the patient’s anatomy. This leads to better fit, comfort, and faster recovery.
b. Faster Prototyping & Product Development
Medical device manufacturers can rapidly prototype and test new designs without relying on costly molds or tooling. This drastically reduces development time and brings innovative products to market faster.
c. Cost-Effective Production
Traditional manufacturing methods often involve high setup costs. 3D printing eliminates the need for molds, enabling low-volume and on-demand production at a fraction of the cost - especially beneficial for startups and R&D teams.
d. Enhanced Surgical Planning
Surgeons use 3D-printed anatomical models to visualize complex procedures before entering the operating room. This improves accuracy, reduces surgery time, and minimizes patient risk.
e. Advancements in Bioprinting
Researchers are now using bioprinting to create tissue structures, such as skin, cartilage, and even organ scaffolds. While still developing, this field holds massive potential for regenerative medicine and organ transplantation.

3. Applications of 3D Printing in the Medical Field
-> Orthopedic Implants: Custom-fit joints, plates, and bone replacements.
-> Dental Solutions: Crowns, bridges, and aligners printed with micron precision.
-> Surgical Guides & Instruments: Patient-specific tools for complex surgeries.
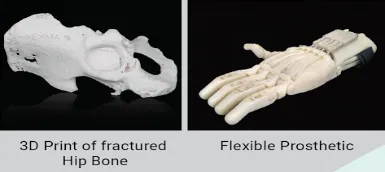
-> Anatomical Models: 3D replicas of organs or bones for training and simulation.
-> Prosthetics: Affordable, lightweight, and comfortable artificial limbs.
-> Drug Delivery Devices: Personalized dosage forms and delivery systems.
4. The Future of 3D Printing in Healthcare
As materials and printing technologies continue to evolve, 3D printing will become even more central to healthcare. The future will likely see:
-> Fully functional bioprinted organs ready for transplantation.
-> Automated hospital-based printing labs for patient-specific parts.
-> Integration with AI and robotics to streamline design and production.
These innovations will lead to a more sustainable, accessible, and patient-focused medical ecosystem.
Summary
The scope of 3D printing in healthcare is truly transformative, empowering innovation across every aspect of the medical field. With advanced biocompatible materials, high-performance thermoplastics, and precision metal printing, we’re driving the next evolution in medical manufacturing. At Vexma Technologies, we’re committed to redefining the future of healthcare through cutting-edge 3D printing solutions.